Galux AI Designs Potent Drugs from Scratch, Upending Pharma R&D
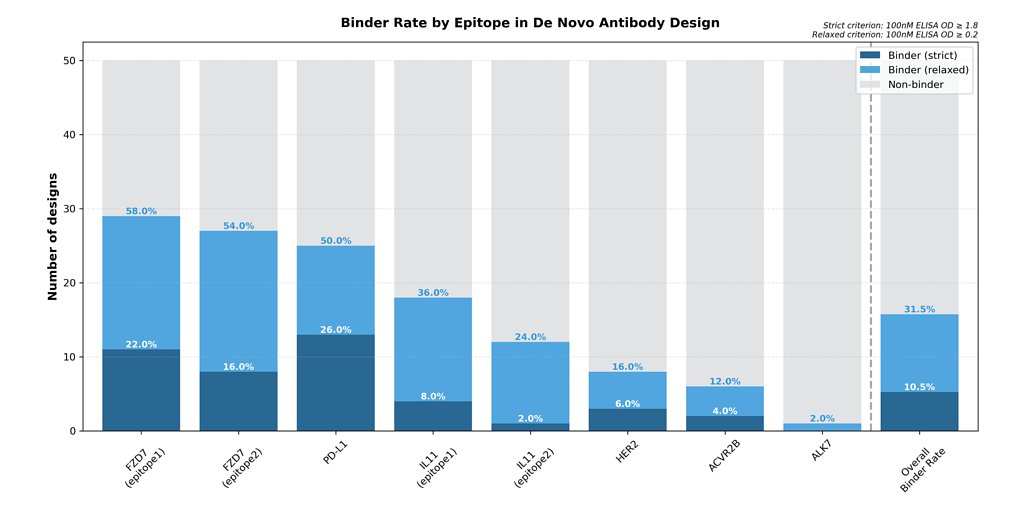
- 31.5% hit rate: Galux's AI achieved a 31.5% success rate in generating therapeutically viable antibodies from just 50 designs per target.
- 10.5% high-affinity binders: 10.5% of AI-generated designs exhibited therapeutically meaningful binding strength, with some reaching picomolar affinity.
- $18 million in funding: Galux has secured $18 million in funding from investors, underscoring market confidence in its technology.
Experts view Galux's AI-driven approach as a transformative shift from probabilistic antibody discovery to rational, high-precision design, significantly accelerating drug development and reducing R&D costs.
From Discovery to Design: How Galux's AI is Rewriting the Rules of Antibody Therapeutics
SEOUL, South Korea – November 26, 2025 – For decades, the discovery of new antibody drugs has been a numbers game—a costly, time-consuming process of sifting through billions of candidates to find a single promising molecule. It’s a model built on probability and persistence. Now, a South Korean biotech firm is demonstrating that the future of drug creation may rely less on chance and more on intentional, intelligent design.
Galux, a pioneer in AI-driven protein engineering, has announced a landmark achievement that signals a fundamental shift in how medicines are made. The company’s platform, GaluxDesign, has successfully generated potent, high-affinity antibodies from a mere fifty AI-generated designs per target. This move from a high-volume screening process to a low-volume, high-precision design process represents a potential sea change for the pharmaceutical industry, promising to dramatically accelerate the development of new therapeutics.
From Billions to Dozens: A New Era of Precision
The traditional method of antibody discovery, known as probabilistic enrichment, involves creating massive libraries of molecules and using high-throughput screening to find one that binds to a specific disease target. This can take months, or even years, and is often followed by a lengthy process of 'affinity maturation' to make the antibody effective enough for therapeutic use.
Galux’s latest study flips this paradigm on its head. By tasking its AI to generate just fifty unique antibody designs for each of eight different disease epitopes, the platform achieved an overall hit rate of 31.5%. More impressively, 10.5% of all AI-generated designs exhibited therapeutically meaningful binding strength, with several candidates reaching picomolar affinity—a level of potency highly sought after in drug development. Crucially, these candidates were validated in a full-length IgG format, the standard structure for most antibody drugs, confirming they behave as viable therapeutic leads without the need for extensive downstream engineering.
“This performance represents more than a numerical improvement in success rate, it reflects a fundamental shift from discovering antibodies to rationally designing them,” said Chaok Seok, CEO of Galux, in a recent announcement. “The ability of GaluxDesign to deliver potent binders within weeks, and without heavy downstream engineering, demonstrates a true transition from stochastic discovery to rational molecular design.”
Building on a Foundation of Atomic Accuracy
This breakthrough in efficiency isn't an isolated event; it's built upon a foundation of rigorously validated science. Galux has been systematically proving its platform's capabilities across a diverse range of challenging therapeutic targets, including PD-L1, HER2, and EGFR—all well-known in cancer therapy. The company has even designed antibodies for targets like ALK7, a protein lacking an experimentally resolved structure, and IL-11, which has no known antibody complex structure, showcasing the AI's power to navigate uncharted biological territory.
In earlier work, the platform produced an anti-PD-L1 antibody with a staggering 9 picomolar affinity, a potency comparable to commercially successful drugs. To prove its AI wasn't just making lucky guesses, Galux used cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to visualize the designed antibody bound to its target. The result was a near-perfect match between the AI's design and the actual physical structure, confirming the platform’s atomic-level precision. This scientific validation, detailed in a pre-print study on BioRxiv, is critical for building trust in AI-generated therapeutics.
By unifying structural accuracy, functional developability, and now small-design efficiency, Galux is making a compelling case that its platform provides a predictable, rather than probabilistic, path to creating new medicines.
The Crowded Field of AI Drug Discovery
Galux is not alone in its quest to revolutionize drug discovery. The field is buzzing with innovation, featuring prominent players like Absci and Generate Biomedicines, which are also using generative AI to create novel protein therapeutics. Even tech giants are entering the fray, with Google's DeepMind spinning out Isomorphic Labs to apply its world-renowned AlphaFold technology to drug design. The collective momentum is undeniable.
“We are witnessing a fundamental shift across the entire industry,” notes one industry analyst. “The question is no longer if AI will design drugs, but how reliably and efficiently it can do so. The ability to achieve high success rates from very small batches of designs, as Galux has shown, is a significant differentiator. It points to a deep, physics-based understanding within the AI, rather than simple pattern matching.”
This distinction is key. While many AI models are trained on existing biological data, Galux claims its platform operates from “first principles,” allowing it to engineer novel solutions for targets that lie outside the realm of known data. This capability could be instrumental in tackling diseases that have so far been considered “undruggable.”
The Business of Breakthroughs: From Lab to Market
The business implications of this technological leap are profound. By drastically reducing the number of candidates that need to be synthesized and tested, the technology could shave months or even years off development timelines and save tens of millions of dollars in R&D costs per program. This efficiency could lower the barrier to entry for developing drugs for rarer diseases and give rise to a new wave of biotech innovation.
Recognizing this potential, investors have taken notice. Galux has secured approximately $18 million in funding from prominent venture capital firms like InterVest and corporate giants such as LG Corp., signaling strong market confidence in its technology. The company’s strategy is multi-pronged: continue advancing the core GaluxDesign platform, develop an in-house pipeline of therapeutic candidates, and forge strategic partnerships with global pharmaceutical companies to co-develop drugs for their most challenging targets.
As Galux moves forward, its focus is expanding. The company aims to apply its high-precision design capabilities to create more complex medicines, such as multi-target antibodies that can attack a disease from multiple angles at once. This next frontier of AI-driven design could unlock entirely new functional architectures for therapeutics, expanding the boundaries of what is possible in modern medicine.
