Agibot Unveils Genie Sim 3.0 to Build Real-World AI in a Digital Twin
At CES 2026, Agibot launched its open-source platform that uses real-world data and LLMs to train robots, aiming to set a new industry standard.
Agibot's Genie Sim 3.0: A Digital Twin to Accelerate Real-World AI
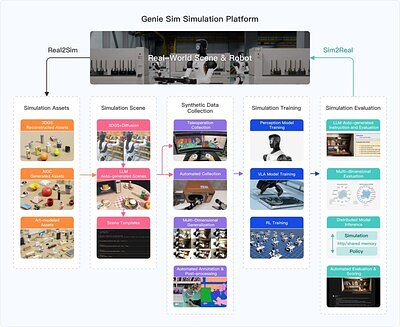
LAS VEGAS, NV – January 06, 2026 – Amidst the dazzling displays of consumer gadgets at CES 2026, robotics company Agibot unveiled a foundational technology that could fundamentally reshape the future of intelligent machines. The company introduced Genie Sim 3.0, a groundbreaking open-source simulation platform designed to train and test embodied AI in hyper-realistic virtual worlds built from real-world data.
By integrating with NVIDIA's powerful Isaac Sim and Omniverse frameworks, Genie Sim 3.0 offers a complete, unified toolchain that promises to slash development times, reduce reliance on costly physical hardware, and establish a much-needed universal standard for evaluating robotic intelligence. This isn't just another simulator; it's a comprehensive ecosystem designed to bridge the stubborn gap between virtual training and real-world performance.
From Real-World Scans to AI-Generated Scenes
A core challenge in robotics has always been the "sim-to-real" problem, where models trained in sterile, artificial simulations fail to perform reliably in the chaotic and unpredictable physical world. Agibot tackles this head-on by building its simulations from the ground up using real-world data. The process begins with capturing detailed scans of physical environments, from complex industrial production lines to sprawling logistics centers, using advanced hardware like Skyland Innovation’s MetaCam handheld 3D laser scanner.
This device combines high-resolution imagery, 360-degree LiDAR point clouds, and precise positioning data to create a dimensionally accurate digital replica. But where Genie Sim 3.0 truly innovates is in its ability to convert these static scans into dynamic, interactive environments. A single 60-second video of an object is enough for the system to generate a simulation-ready, physics-enabled asset. This dramatically accelerates the traditionally laborious process of building virtual worlds.
Further amplifying this capability is the platform's pioneering use of Large Language Models (LLMs). Developers can now describe a desired scene or task variation in natural language—for instance, "create a warehouse scene with randomly stacked boxes on a conveyor belt"—and the system automatically generates the structured environment, complete with thousands of semantic variations. This LLM-driven approach moves beyond manual scripting, enabling the rapid creation of the vast and diverse datasets needed to train robust, generalizable AI models that can adapt to novel situations.
Setting a New Standard for Benchmarking
For years, the embodied AI research community has lacked a common yardstick. Progress has been difficult to track and compare, with different teams using bespoke evaluation metrics that often focus on simple success or failure rates. This makes it nearly impossible to understand why a model fails or where its specific strengths and weaknesses lie.
Agibot aims to solve this with the Genie Sim Benchmark, the core evaluation module of the platform. Moving far beyond single-metric scores, the benchmark provides a comprehensive capability profile for any given AI model. It includes over 200 distinct tasks spread across more than 100,000 unique scenarios, testing everything from basic manipulation and spatial reasoning to complex, long-horizon planning and commonsense understanding.
This multi-dimensional evaluation framework provides a fine-grained analysis of a model's performance, clearly outlining its limitations and suggesting pathways for optimization. By open-sourcing the benchmark alongside a massive dataset of over 10,000 hours of synthetic data—including RGB-D vision, stereo vision, and whole-body kinematics—Agibot is not just offering a tool, but proposing an industry standard. This could foster a more collaborative and rigorous research environment, allowing developers worldwide to compete and innovate on a level playing field, much like standardized benchmarks did for computer vision and natural language processing.
Revolutionizing the Industrial Factory Floor
While the implications for academic research are profound, the most immediate impact of Genie Sim 3.0 may be felt in the industrial sector. The platform is the first of its kind to integrate real industrial-scene datasets directly into its training and evaluation pipelines. Agibot has already created 1:1 digital twins of logistics centers, power inspection sites, and manufacturing facilities.
This capability aligns perfectly with the growing industry trend of "Simulate-then-Procure." Companies can now design, test, and optimize entire robotic work cells in a high-fidelity virtual environment before a single piece of physical hardware is ordered or installed. An algorithm for a new pick-and-place robot can be validated across millions of cycles and countless object variations without risking damage to a physical prototype or disrupting an active production line.
This drastically reduces the cost, time, and risk associated with deploying new automation technologies. The intelligent data-collection toolkit further streamlines this process, supporting both automated task programming and low-latency teleoperation for capturing human demonstrations. An integrated recovery mechanism even allows data collection to resume automatically after a simulated task failure, minimizing human intervention and maximizing efficiency. By enabling end-to-end model development and testing in a virtual space, Genie Sim 3.0 empowers industries to innovate faster and deploy robots with far greater confidence.
The Democratizing Power of Open Source
Perhaps the most strategic element of Agibot's announcement is its commitment to open source. The entire platform—its assets, datasets, and source code—is available on GitHub. This move, combined with its foundation on NVIDIA's open-source Isaac Sim reference framework, positions Genie Sim 3.0 not as a proprietary walled garden, but as a community-driven ecosystem.
By lowering the barrier to entry, Agibot is empowering startups, academic labs, and individual researchers who may lack the resources to build such sophisticated simulation infrastructure from scratch. This democratization of advanced tools could spark a wave of innovation in embodied intelligence, as a global community of developers contributes to the platform, builds upon its foundation, and pushes the boundaries of what's possible.
The deep integration with the NVIDIA Omniverse ecosystem provides a robust, physically accurate rendering and simulation engine, ensuring that the virtual worlds are not just visually convincing but also behave according to the laws of physics. As robots, particularly humanoids, become more complex, this level of fidelity is no longer a luxury but a necessity for effective training. With Genie Sim 3.0, Agibot is making a bold bet that the future of robotics will be built collaboratively, in virtual worlds that are nearly indistinguishable from our own.
📝 This article is still being updated
Are you a relevant expert who could contribute your opinion or insights to this article? We'd love to hear from you. We will give you full credit for your contribution.
Contribute Your Expertise →